Micronutrients play a huge role in health and performance. Be it vitamins or minerals, they have such major roles to play though they are required in micro quantities.
Vitamin D is one such important, fat-soluble vitamin. It is called the sunshine vitamin.
A fun fact about this vitamin is that this is the only vitamin that the body can synthesise on its own, unlike the other vitamins.
Is Vitamin D a hormone?
Ideally, Vitamin D is an inaccurate name, a misnomer. It is not a true vitamin because it can be synthesized externally through ultraviolet exposure of the skin to the sun. It is a fat-soluble hormone that comes in 3 forms [19]. Vitamin D is more of a multifunctional hormone or prohormone[2].
Sources of Vitamin D
The other sources of Vitamin D apart from sunlight include:[1]
- Mushrooms
- Eggs
- Oily fishes- such as salmon, sardines, herring and mackerel.
- Supplements
- Fortified foods- ready-to-eat breakfast cereals, milk, orange juice, infant formula, yoghurt, margarine, butter, cheese

Functions of Vitamin D for athletes and the general population [3,17]
Vitamin D is well known for its influence on the bones. However, it is not limited to that. Vitamin D also has multi-functions:
- Acts as a pro-hormone in the body
- Regulates the parathyroid hormone
- Regulates uptake of calcium and phosphorus
- Enhances immunity
- Improves cardiovascular system
- Prevents inflammation
Risks of Vitamin D Deficiency for athletes and the general population[3]
A deficiency in Vitamin D can lead to:
- Rickets where there is softening and weakening of bones in children
- Osteomalacia is softening of bones in adults
- Osteoporosis and osteoporotic-related fractures are caused due to changes in the quality of bone and its structure.
- Increase in cancers (colon, prostate, and breast)
- Depression: Vitamin D is a key nutrient for your mental and physical health. Studies have found that low vitamin D levels are linked to depression and that taking vitamin D supplements may help improve depression symptoms in people with low vitamin D levels[16].
- Increase in infections, especially upper respiratory tract infections.
- Pain (musculoskeletal, cancer, fibromyalgia)
Vitamin D recommendations [3]
The recommended Vitamin D intake levels of the Institute of Medicine
| Age | Recommended Intake (IU/day) |
| Children (0–18 years) | 400–600 |
| Adults (19–70 years) | 600 |
| Older Adults (>70 years) | 800 |
| Pregnancy/Lactation | 600 |
The toxicity of Vitamin D might be caused due to excess consumption of supplements for a long period of time. The main consequence of vitamin D toxicity is a buildup of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause nausea and vomiting, weakness, and frequent urination. Vitamin D toxicity might progress to bone pain and kidney problems, such as the formation of calcium stones[15, 17].
Best time for sun exposure for the synthesis of Vitamin D
Vitamin D from sunlight is best synthesised between 10 am to 3 pm when the rays of the sun are concentrated (UV-B) [1]. A 15 to 20-minute exposure to the sun during this period without sunscreen can synthesise over 10,000 IU of Vitamin D in light-skinned people. However, even those who spend the most time outdoors might require supplementation in case of insufficiency or deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency is defined as <20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L), insufficiency is defined as 20–32 ng/mL (50–80 nmol/L), and optimal levels are >40 ng/mL (100 nmol/L) [3,17].
Vitamin D and women
The ways in which Vitamin D can help women are: [18]
- It can help regulate insulin levels in the body
- It can control cholesterol levels
- It can help with the regular menstrual cycle
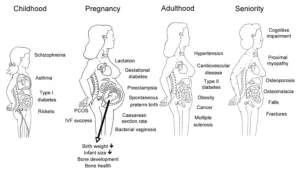
The above image shows the health implications of Vitamin D deficiency in women. A proper intake of Vitamin D through foods and sunlight can prevent the frequency of such problems in women[18].
How research shows the effects of Vitamin D on athletes?
The levels of Vitamin D in the blood are seen to be lowest in March and highest in September[4].
A supplementation of Vitamin D has shown improvement in hand grip strength[12]. Athletes with excess fat may be at higher risk for Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency[13]. Very low Vitamin D levels in swimmers may lead to respiratory infections[14].
The amount of Vitamin D in women can also affect their bone mineral density. Sufficient Vitamin D can also improve aerobic performance in athletes. [17]
Vitamin D and Calcium
As seen earlier, Vitamin D interacts with calcium in the body. They are the two most important nutrients for bone health.
Calcium is a well-known mineral that majorly keeps the bone healthy. Rich sources of calcium per 100g are drumstick leaves/ moringa powder, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, ragi, milk, and jaggery.

Vitamin D and calcium play pivotal roles in the prevention of fractures, especially in women. It is Vitamin D that is responsible for uptake and regulation of calcium in the bones and the blood. Sufficient Vitamin D levels ensure proper calcification of the bones and thereby can help prevent calcium deficiency.
In this light, it is necessary to consume Vitamin D-rich foods alongside calcium-rich foods.
Conclusion
It can therefore be concluded that Vitamin D is very essential in so many aspects of health and performance, more so for female athletes.
Thus it is important for female athletes to
- keep an eye on the serum levels of Vitamin D at least once in 6 months,
- ensure sufficient dietary intake of Vitamin D and sun exposure as per guidelines.
Consulting a nutritionist/ a medical practitioner before administration of vitamin supplements is very essential as the results always need to be correlated clinically.
References
- Khazai N, Judd SE, Tangpricha V. Calcium and vitamin D: skeletal and extraskeletal health. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2008 Apr;10(2):110-7. doi: 10.1007/s11926-008-0020-y. PMID: 18460265; PMCID: PMC2669834.
- Ellison DL, Moran HR. Vitamin D: Vitamin or Hormone? Nurs Clin North Am. 2021 Mar;56(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2020.10.004. Epub 2020 Dec 28. PMID: 33549285.
- Ogan D, Pritchett K. Vitamin D and the athlete: risks, recommendations, and benefits. Nutrients. 2013 May 28;5(6):1856-68. doi: 10.3390/nu5061856. PMID: 23760056; PMCID: PMC3725481.
- Maruyama‑Nagao, A., Sakuraba, K., & Suzuki, Y. (2016). Seasonal variations in vitamin D status in indoor and outdoor female athletes. Biomedical Reports, 5, 113-117. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.671
- Vitamin D sources image retrieved from https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQMW8sOrX3TFbCjr89lmezcINC5pD_evUMrpA&usqp=CAU
- Moringa powder image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Forigin.club%2Fmedia%2Fcatalog%2Fproduct%2Fcache%2F86eaafd287624d270d87c663dd3976d5%2Fm%2Fo%2Fmoringa_powder_2.jpg&tbnid=3t1GhrJipz-MBM&vet=12ahUKEwj6hsn1oL6AAxXl5zgGHTbJBTAQMygBegUIARD5AQ..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Forigin.club%2Fmoringa-powder-200-gm.html&docid=Uk8a68HAUVjZPM&w=700&h=700&q=moringa%20powder&ved=2ahUKEwj6hsn1oL6AAxXl5zgGHTbJBTAQMygBegUIARD5AQ
- Poppy seeds image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Ftrvcashews.com%2Fshop%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2021%2F05%2FPoppy-Seeds.jpg&tbnid=ZnE02ryrfSCSIM&vet=12ahUKEwicwvmUob6AAxUHm2MGHff1CcsQMygAegUIARDwAQ..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Ftrvcashews.com%2Fshop%2Fproduct%2Fpoppy-seeds%2F&docid=sxWe8C0utM61BM&w=600&h=600&q=poppy%20seeds&ved=2ahUKEwicwvmUob6AAxUHm2MGHff1CcsQMygAegUIARDwAQ
- Sesame seeds image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.britannica.com%2F66%2F212766-050-FF1A49A0%2Fsesame-seeds-wooden-spoon.jpg&tbnid=wqYnyrlcj8nS-M&vet=12ahUKEwjK-Kyvob6AAxVKm2MGHZyWAEkQMygAegUIARD1AQ..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.britannica.com%2Fplant%2Fsesame-plant&docid=LiKQ19rEIQFEMM&w=1600&h=1148&q=sesame&ved=2ahUKEwjK-Kyvob6AAxVKm2MGHZyWAEkQMygAegUIARD1AQ
- Ragi image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http%3A%2F%2Fnaturallyyours.in%2Fcdn%2Fshop%2Farticles%2Fragi1.jpg%3Fv%3D1659348826&tbnid=-KU7v30bMj-NPM&vet=12ahUKEwiWusPfob6AAxVL_zgGHZ0HB7AQMygAegUIARCIAg..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fnaturallyyours.in%2Fblogs%2Fblog%2F10-health-benefits-of-ragi&docid=KmWD3wkFTHTtyM&w=2240&h=1260&q=ragi&ved=2ahUKEwiWusPfob6AAxVL_zgGHZ0HB7AQMygAegUIARCIAg
- Milk image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.eatthis.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2Fsites%2F4%2F2020%2F02%2Fglass-of-milk.jpg%3Fquality%3D82%26strip%3D1&tbnid=s8_ivPnBd5XeJM&vet=12ahUKEwjZ-un7ob6AAxW15DgGHc5dAfQQMygaegUIARC-Ag..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.eatthis.com%2Fwhat-happens-body-drink-milk%2F&docid=Pmadq71DK8A0TM&w=1200&h=879&q=milk&ved=2ahUKEwjZ-un7ob6AAxW15DgGHc5dAfQQMygaegUIARC-Ag
- Jaggery image retrieved from https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.ruraltreasures.com%2Fcdn%2Fshop%2Farticles%2FNbmkT7xqOx5VE9X8ZzK5TXIEvvJ0bpwnhJfEi2gd.jpg%3Fv%3D1644053684&tbnid=TBkC4gZLmSLQkM&vet=12ahUKEwjjsdinor6AAxUz7DgGHZ3yByMQMygDegUIARD_AQ..i&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ruraltreasures.com%2Fblogs%2Fnews%2Fwhat-is-jaggery-types-of-jaggery-and-its-benefits&docid=mNpqwC5uqxV2YM&w=870&h=581&q=jaggery&ved=2ahUKEwjjsdinor6AAxUz7DgGHZ3yByMQMygDegUIARD_AQ
- Pritchett, K., Pritchett, R. C., Stark, L., Broad, E., & LaCroix, M. (2019). Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on 25(OH)D Status in Elite Athletes With Spinal Cord Injury. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 29(1), 18-23. Retrieved Jul 29, 2023, from https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2017-0233
- Heller, J. E., Thomas, J. J., Hollis, B. W., & Larson-Meyer, D. E. (2015). Relation Between Vitamin D Status and Body Composition in Collegiate Athletes. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 25(2), 128-135. Retrieved Jul 29, 2023, from https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0250
- Dubnov-Raz, G., Hemilä, H., Cohen, A. H., Rinat, B., Choleva, L., & Constantini, N. W. (2015). Vitamin D Supplementation and Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adolescent Swimmers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatric Exercise Science, 27(1), 113-119. Retrieved Jul 29, 2023, from https://doi.org/10.1123/pes.2014-0030
- What is vitamin D toxicity? Should I be worried about taking supplements?. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/vitamin-d-toxicity/faq-20058108#:~:text=The%20main%20consequence%20of%20vitamin,the%20formation%20of%20calcium%20stones
- Is a Vitamin D Deficiency Causing Your Depression? Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/depression-and-vitamin-d#connection
- de la Puente Yagüe, M., Collado Yurrita, L., Ciudad Cabañas, M. J., & Cuadrado Cenzual, M. A. (2020). Role of Vitamin D in Athletes and Their Performance: Current Concepts and New Trends. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0250Nutrients, 12(2), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020579
- Grundmann, M., von Versen-Höynck, F. Vitamin D – roles in women’s reproductive health?. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 9, 146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-9-146
- Demer LL, Hsu JJ, Tintut Y. Steroid Hormone Vitamin D: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2018 May 25;122(11):1576-1585. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311585. PMID: 29798901; PMCID: PMC6122607.

Harshavardhini S is a Sports Nutritionist with a Master’s in sports nutrition from ICMR- National Institute of Nutrition, with a keen interest in female athletes- health and performance.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/harshavardhini-s-017360233